What is "Concurrent Connections" in Web Systems?
"Concurrent connections" is a term often used in web system development, but it is frequently misused without a clear definition. Here, we will create a strict definition including several related terms.
- Maximum Login Users: After login, session information is created and occupies certain memory. Depending on the system method, if session memory is large, pay attention to the number of users logging in within the session timeout period.
- Maximum Concurrent Connections: TCP connections are considered "connected" from "Established" to "Closed". The number of open connections at any given time is the concurrent connection count. One screen operation generates two connections (JSP and various static content). After output completion, the connection is maintained for 15 seconds.
- Maximum Concurrent Executions: The number of requests the server can process simultaneously.
If Proxy, FireWall, etc. have caching capabilities, connections to static content may not reach the WEB server. And to be more precise, it's not 2 but 1.X.
System Concept Diagram
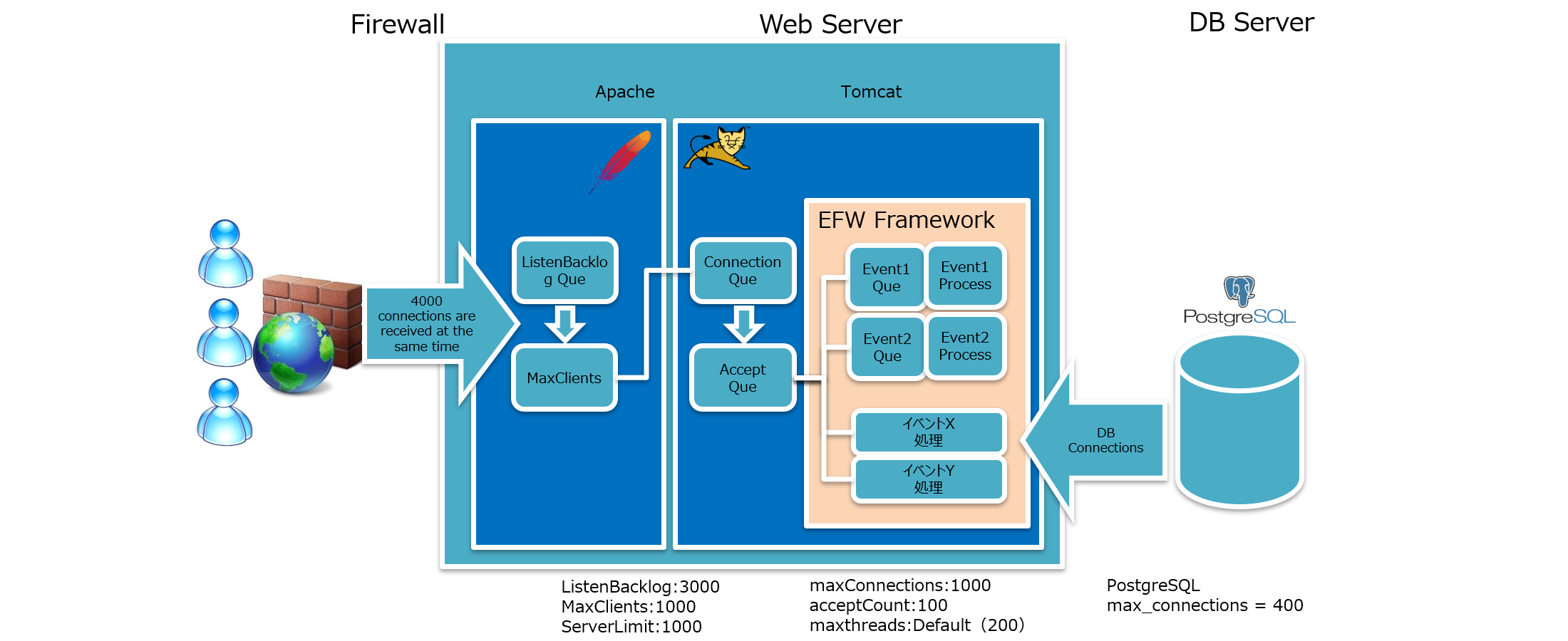
| Configuration Item | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ListenBacklog | 3000 | Maximum connection wait queue number for queuing requests of established TCP connections |
| maxConnections | 1000 | Maximum number of concurrent connections the server accepts and processes |
| acceptCount | 100 | Maximum queue length for incoming connection requests when all possible request processing threads are in use |
| MaxClients | 100 | Number of concurrent requests that can be responded to |
| maxthreads | 200 (default) | Maximum number created for request processing (maximum concurrent executions) |
| ServerLimit | 1000 | Maximum configurable value for MaxClients (maximum during Apache process execution, limited to 20000 or less) |
System Concept Diagram Explanation
When there are many connections from clients:
- First stored in Apache's ListenBacklog queue,其中1000 connections are passed to Tomcat.
- Tomcat receives connection requests and stores them in the Connection queue.
- 100 connections are moved from the Connection queue to the Accept queue for processing.
- Subsequent connection requests fill the vacancies in the Connection queue.
- To ensure the Connection queue does not exceed its maximum value, match the values of MaxClients and maxConnections.
When processing connection requests in the Connection queue with the EFW framework:
- For heavy processing, set a concurrently processable queue for each event. When the queue maximum is reached, return an error.
- For light processing, do not set a concurrently processable queue.
There are two types of errors when the event queue maximum is reached:
- If retry is allowed, display an error message and count down for 30 seconds.
- If set to no retry, only display an error message.
Error Scenarios
ListenBacklog Queue Overflow
When the server connections are full, new operations will display the following error message:
Connection error: The server is busy. Please try again after a while.
Event Queue Overflow (Retry Allowed)
When heavy operations are restricted, the following countdown message will be displayed (30-second count). Retry allowed.
The system is busy. Please wait until the operation becomes available.
Event Queue Overflow (No Retry)
When operations are restricted, the following busy message will be displayed. No retry.
This function is busy. Please wait for a while.
Configuration Locations
Various parameters can be adjusted in the following configuration files:
- Apache Configuration (httpd.conf): ListenBacklog, MaxClients, ServerLimit
- Tomcat Configuration (server.xml): maxConnections, acceptCount, maxthreads
- EFW Configuration (efw.properties): Event queue size, retry settings
- PostgreSQL Configuration (postgresql.conf): max_connections
To handle high-load environments, these values need to be appropriately adjusted according to system requirements.